System of Control Engineering Systems (SMIS)
What is a structured system for monitoring and managing engineering systems of buildings and structures SMIS?
Definition, according to GOST R 22.1.12-2005: A structured system for monitoring and managing engineering systems of buildings and structures SMIS is a software and hardware system designed to monitor technological processes and processes for ensuring the functioning of equipment directly at potentially hazardous facilities, in buildings and structures and transferring information about their condition via communication channels to the dispatching services of these facilities for subsequent processing in order to assess, prevent and eliminate the consequences of destabilizing factors in real time, as well as to transmit information about the forecast and the fact of emergencies, incl. caused by terrorist acts, into the Unified Duty Dispatch Service (UDDS).
In accordance with GOST R 22.1.12-2005, the purpose of creating an SMIS is to ensure the guaranteed stability of the functioning of life support systems, safety and technological processes of the required quality at a controlled potentially dangerous object, building and structure. SMIS acts as a means of information support for decision-making by a dispatcher under conditions of destabilizing factors.
Objects of the corresponding categories should be equipped with SMIS, informationally coupled with the automated systems of the RSChS day-to-day management bodies for the prevention and elimination of emergencies, incl. caused by terrorist acts.
SMIS should ensure the prevention of emergency situations, the classification of which is determined by the Government of the Russian Federation
In accordance with clause 4.9 of GOST R 22.1.12-2005, SMIS are subject to mandatory installation on the following categories of objects:
- nuclear and / or radiation hazardous facilities (nuclear power plants, research reactors, fuel cycle enterprises, storage facilities for temporary and long-term storage of nuclear fuel and radioactive waste);
- objects on which:
obtained, used, processed, formed, stored, transported, destroyed hazardous substances in quantities exceeding the maximum established by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
destruction, burial of chemical and other hazardous waste is carried out;
there are large warehouses for storage of oil and oil products (over 20 thousand tons) and isothermal storage facilities for liquefied gases;
melts of ferrous and non-ferrous metals and alloys based on these melts are obtained;
mining, mineral processing, as well as underground operations, including underground and open-pit mining and processing (enrichment) of solid minerals (depth of development over 150 m);
stationary cable cars and funiculars are used;
produce, receive or process liquid-phase or solid products with explosive properties and prone to spontaneous decomposition with a possible explosion energy equivalent to 4.5 tons of trinitrotoluene;
- communication facilities, which are especially dangerous, technically complex in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation in the field of communication;
- power lines and other power grid facilities with a voltage of 330 kV and more;
- objects of space infrastructure;
- airports and their infrastructure facilities;
- objects of public railway transport infrastructure;
- subways;
- seaports, with the exception of specialized seaports designed to service sports and pleasure craft;
- thermal power plants with a capacity of 150 MW and above;
- facilities for the development of oil fields on the shelf of the seas;
- main gas, oil and product pipelines;
- objects of gas distribution systems where natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas is used, stored, transported;
- hydraulic structures of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd classes;
- large industrial facilities with more than 10 thousand people employed;
- capital construction objects, the design documentation of which provides for at least one of the following characteristics:
height more than 100 m;
spans more than 100 m;
the presence of a console more than 20 m;
deepening of the underground part (in whole or in part) below the planned level of the earth by more than 10 m;
the presence of structures and structural systems for which non-standard calculation methods are applied taking into account physical or geometric nonlinear properties or special calculation methods are developed;
- objects with a maximum estimated occupancy of 500 people. and more: entertainment, sports facilities, multifunctional office and shopping and entertainment complexes, healthcare facilities, hotels;
- life support facilities: installations, warehouses, storage facilities, hydraulic and engineering protective structures, communications, the destruction (damage) of which can lead to disruption of the normal life of people (interruption of the supply of water, gas, heat, electricity, flooding, damage to residential areas, failure sewage systems and wastewater treatment) and, as a result, to an emergency.
SMIS is an automated system of the facility that provides automatic monitoring and warning of emergencies regardless of the facility operation services.
SMIS should ensure control of the following main destabilizing factors:
- the occurrence of a fire;
- disturbances in the heat supply system, heating, hot and cold water supply;
- violations in the supply of electricity;
- violations in the gas supply;
- refusal in the operation of elevator equipment;
- unauthorized entry into office premises;
- increased level of radiation, maximum permissible concentration of emergency chemically hazardous substances; biohazardous substances; explosive concentrations of gas-air mixtures;
- flooding of premises, drainage systems and technological pits;
- gas leaks;
- deviations from the normative parameters of technological processes that can lead to emergency situations;
- changes in the state of the foundation, construction (engineering and technical) structures of buildings and structures;
- failure of the emergency protection, safety and fire protection systems;
- engineering protection structures;
- changes in the state of areas of possible mudflows, landslides, avalanches in the operation area of the monitoring object.
SMIS should provide:
- forecasting and preventing emergency situations by monitoring the parameters of the processes of ensuring the functioning of objects and determining the deviations of their current values from the normative ones;
- continuity of collection, transmission and processing of information about the values of the parameters of processes to ensure the functioning of objects;
- formation and transmission of formalized operational information on the state of technological systems and changes in the state of engineering and technical structures of objects to the duty and dispatching services of the object;
- formation and transmission of a formalized emergency message at facilities, incl. caused by terrorist acts, to the RSChS day-to-day management bodies;
- automated notification of an accident, emergency and necessary evacuation actions;
- automated notification of relevant specialists responsible for the safety of facilities;
- documentation and registration of emergency situations, as well as actions of duty and dispatching services of objects.
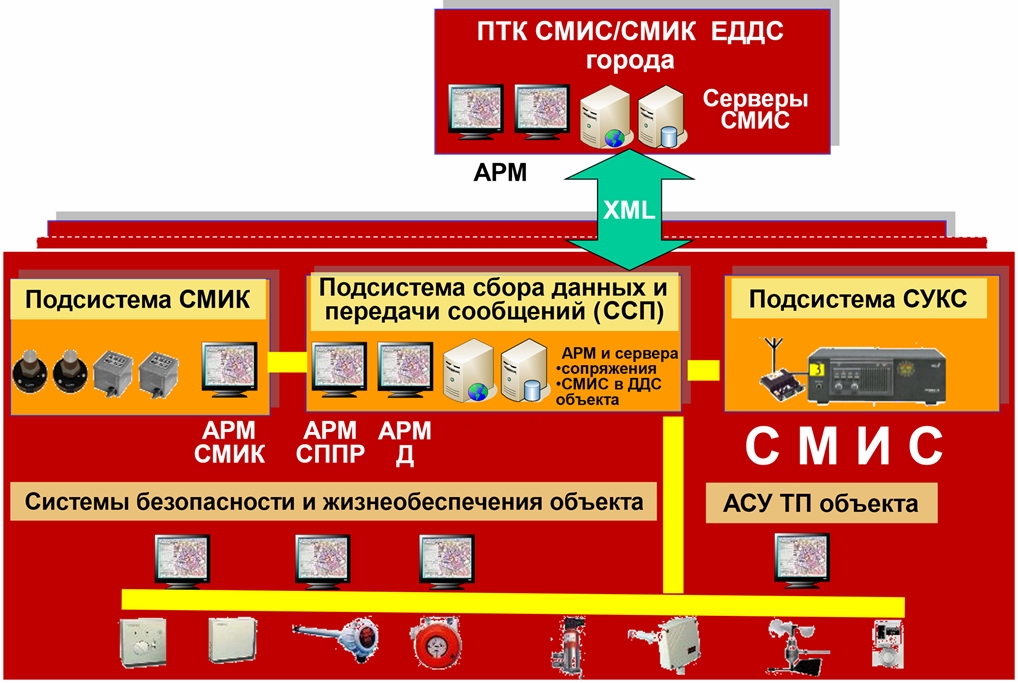
The SMIS includes the following systems:
• data collection and message transmission system (SSP) - monitors SMIS subsystems, technological processes and engineering systems of the facility, as well as informs the facility's DDS, operational dispatch structures (EDDS) of the municipal formation about the occurrence of pre-emergency, emergency, emergency situations (ES), fires;
• communication and management system in crisis situations (CMS) - provides management of units for liquidation of the consequences of accidents, fires, emergencies, including those caused by terrorist acts, and includes:
◦ system of operational, emergency telephone communication;
◦ operational radio communication system of city security services and emergency services;
• monitoring system for engineering (supporting) structures, hazardous natural processes and phenomena (SMIC) - real-time automatic monitoring of changes in the state of supporting structures, the development of hazardous geological processes and provides periodic monitoring of the technical condition of the supporting structures of the object, dangerous geological processes.
Objects of SMIS control:
• Subsystems of life support and safety:
◦ heat supply;
◦ ventilation and air conditioning, microclimate control;
◦ water supply and sewerage;
◦ power supply;
◦ gas supply;
◦ engineering and technical complex of fire safety of the facility;
◦ elevator equipment;
◦ voice notification system;
◦ security alarm and video surveillance system;
◦ detection system for increased levels of radiation, emergency chemical hazardous substances, biologically hazardous substances, significant concentrations of toxic and explosive gases, etc.;
◦ a system for transmitting information about the presence of current control by the regular maintenance service of the facility or network of facilities.
• Engineering and technical structures (structural elements) of potentially hazardous objects, buildings and structures.
• Technological equipment of the object.
Stages of SMIS development
• Development of special technical conditions for the creation and operation (STU) of the SMIS facility;
• Development of technical specifications for SMIS design, its coordination and approval;
• Development of design documentation for SMIS;
• Maintenance of SMIS project documentation upon receipt of approval in the state expertise;
• Development of working documentation for the SMIS (including the development of a procedure for the on-duty dispatch service of the facility and the duty bodies of daily management of the RSChS upon receipt of SMIS messages, development of programs and test methods for the SMIS), obtaining the necessary approvals for documentation;
• Construction and installation works for SMIS;
• Start-up and adjustment works on SMIS, including connection of the SMIS facility to the daily management bodies of the RSChS;
• Testing and commissioning of the SMIS facility for permanent operation.
SMIS software and hardware must be certified in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The software and hardware of SMIS objects must have confirmation of compliance with the technical requirements for interfacing with automated systems of the daily management bodies of the RSChS in accordance with.
The design and construction of SMIS should be carried out by organizations that have certificates of self-regulatory organizations for admission to work in the field of civil defense measures, measures to prevent natural and man-made emergencies. Specialists of these organizations must have state diplomas (certificates, certificates) on special training (advanced training) in educational programs in this field, including SMIS.
Normative and technical base for the creation and operation of SMIS:
Basic provisions
1. Objects of social and domestic, residential and other purposes should be equipped with SMIS, informationally coupled with automated systems of duty dispatching services (hereinafter - DDS) of objects and EDDS in order to prevent and eliminate emergencies, including those caused by terrorist acts.
2 SMIS is created in order to ensure the guaranteed stability of the functioning of the system of life support processes of the required quality at the controlled facilities and act as a means of information support for decision-making on the prevention and elimination of emergencies, including those caused by terrorist acts, dispatchers of DDS facilities and UDDS under conditions of destabilizing factors ...
In terms of emergency prevention, SMIS is an integral element of the automated systems of the facility, developed according to GOST 34.003, GOST 34.601, GOST 34.603.
3 SMIS is built on the basis of software and hardware tools that monitor technological processes and processes of ensuring the operation directly at the facilities and ensure the transfer of information about their state through communication channels in the DDS of these facilities for subsequent processing in order to assess, predict and eliminate the consequences destabilizing factors in real time, as well as for transmitting information about the forecast and the fact of emergencies, including those caused by terrorist acts, to the UDDS.
4 Objects of control, and in some cases, control, should be subsystems of life support and safety.
The objects of control should be engineering structures (structural elements) of objects.
5 SMIS should ensure control of the main destabilizing factors (fires, accidents and malfunctions in the engineering and technical systems of facilities, violations of the state of engineering and technical structures, disruption of technological systems, gas pollution, terrorist manifestations.
6 SMIS should provide: forecasting and prevention of emergencies, the continuity of collection, transmission and processing of information, the formation and transmission of formalized operational information, the formation and transmission of a formalized message about emergencies at facilities, automated or forced launch of a system for alerting the population about an emergency that has occurred and the necessary actions for evacuation, automated or compulsory notification of relevant specialists, automated or compulsory launch of emergency warning or elimination systems according to certain algorithms for a specific facility and a specific type of emergency, documentation and registration of emergency situations, as well as the actions of DDS facilities.
7 The SMIS should include a set of measuring instruments, automation equipment and actuators, a multifunctional cable system, an information transmission network, an automated dispatch control system for engineering systems of facilities;
8 EDDS in terms of solving security problems of facilities should solve the following main tasks:
- receiving information from the SMIS about the forecast or occurrence of an emergency, including that caused by a terrorist act;
- analysis and assessment of the reliability of the information received about the emergency, bringing it to the DDS, whose competence includes responding to the received message;
- processing and analysis of data on emergencies, determining its scale and clarifying the composition of the DDS involved in responding to emergencies, their notification of the transfer to the highest modes of functioning of the link (subsystem) of the RSChS;
Monitoring, warning, prevention of accidents, fires, explosions, emergencies in the municipal level of the RSChS according to SMIS reports
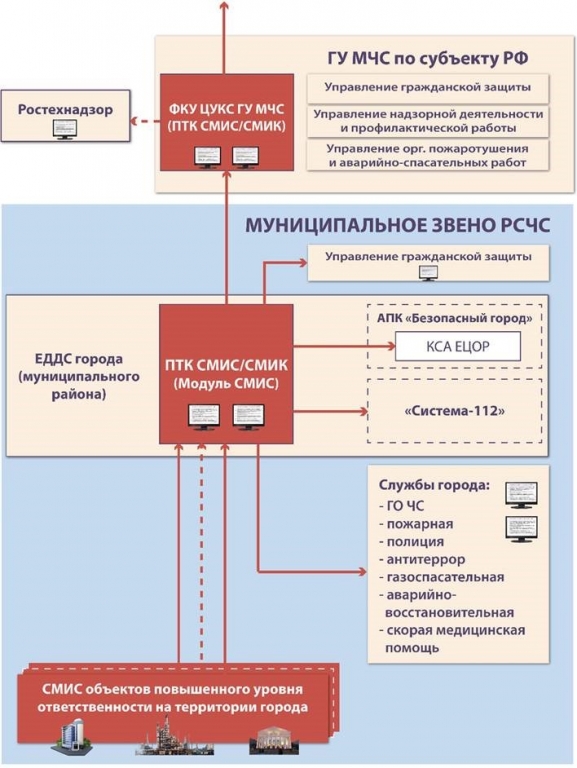
- operational management of emergency rescue services, fire, fire and rescue and emergency rescue teams, setting and communicating to them the tasks of localizing and eliminating the consequences of emergencies, including those caused by terrorist acts, taking the necessary emergency measures and decisions (within the limits established by higher authorities);
- generalization, assessment and control of the data of the situation, the measures taken to eliminate the emergency, clarification and correction (as appropriate) of the options for solutions for the elimination of emergencies that were previously developed and agreed with the city services;
- constant informing of the DDS involved in the elimination of emergencies, the subordinate forces of constant readiness about the situation, taken and recommended measures;
- submission of reports (reports) to higher management bodies under subordination on the threat or occurrence of an emergency, including caused by a terrorist act, the current situation, possible solutions and actions to eliminate emergency situations (based on previously prepared and agreed plans);
- communicating the tasks set by the higher authorities of the RSChS to the DDS and subordinate forces of constant readiness, monitoring their implementation and organizing interaction;
- generalization of information about emergencies that have occurred (per day of duty), the progress of work on their elimination and submission of relevant reports on subordination.
The modes of operation and the composition of the EDDS must comply with the requirements of GOST R 22.7.01.
9 SMIS are subject to mandatory installation at potentially dangerous, especially dangerous, technically complex and unique facilities.
10 Equipment of SMIS facilities should be carried out during:
- design, construction and installation works - for newly built
objects;
- scheduled overhaul - for facilities in operation.
Acceptance of facilities without equipment for their SMIS is not allowed.
11 The SMIS software and hardware must be certified
in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
12 Training of specialists in the creation of an SMIS, work on the design, installation, acceptance and operation of an SMIS should be carried out in accordance with the SMIS methodology and regulatory documents.
General technical requirements
1 Requirements for structure and function
SMIS should provide automated control and management, have a modular structure and be "open", allow the possibility of integration with other information monitoring and control systems.
The SMIS should provide for automatic - manual and remote - local operating modes.
SMIS should have an open architecture, allow for subsequent expansion, both in the number of automation objects and in the number of functions, and also be ready for integration with other monitoring and control systems.
SMIS should be based on structured information cable networks.
SMIS should have a hierarchical multi-level structure:
Level 1 - Structured Information Cabling System.
level 2 - primary sensors and actuators, as well as devices for matching the signals of primary sensors with the inputs of data collection controllers;
level 3 - data collection controllers (remote input-output modules), programmable logic controllers, intelligent equipment control panels, engineering systems control workstations.
level 4 - SMIS input / output servers. The SMIS server should contain the means of organizing the exchange of information with dispatching workstations. The SMIS server must transmit operational data to the facility personnel through other information networks;
level 5 - automated workstations of dispatchers.
2 Requirements for reliability
The service life of the system should be at least 10 years, taking into account the replacement of faulty and worn out components. The warranty period is 18 months. from the moment of commissioning.
Mean time between failures of SMIS is at least 10,000 hours.
The average recovery time for the SMIS is no more than 30 minutes.
To quickly troubleshoot equipment, there must be
the necessary set of spare parts, tools and
accessories.
3 Safety requirements
The system should have means of protection against operator errors of personnel that can lead to accidents of facility engineering subsystems.
The system should have a means of documenting the actions of SMIS operators.
The components included in the SMIS should not have a harmful effect on human health.
4 Ergonomic requirements
SMIS equipment should be placed in metal or plastic cabinets (shields) that provide easy access to controls.
Automated workstations of dispatchers and service managers must be equipped with monitors with a screen diagonal of at least 395 mm, having a resolution of at least 1280 x 1024 at a proportional scan with a frame rate of at least 75 Hz.
5 Requirements for information protection
Information protection of SMIS - according to the regulatory document.
6 Requirements for protection against the influence of external influences
SMIS equipment should be placed in metal or plastic cabinets (shields) providing a protection class of at least IP40 according to GOST 14254.
Technical means must be operable under atmospheric influences, corresponding to the technical conditions for these means.
7 Requirements for standardization and unification
Design solutions should be unified for all objects of automation.
8 Compatibility requirements
The system must use equipment that is compatible with both physical interfaces and information protocols. As physical interfaces and information protocols, only open protocols and standardized interfaces are allowed, which in terms of their functions correspond to the requirements issued within the framework of the initial permitting documentation for the object.
9 Environmental requirements
The components included in the SMIS and the materials from which they are made should not have a chemical, biological, radiation, mechanical, electromagnetic and thermal effect on the environment.
The components included in the SMIS, when stored or used for their intended purpose, should not emit harmful, polluting or toxic substances into the environment.
Wastes generated during the manufacture of components included in the SMIS and components included in the SMIS after the expiration date are subject to destruction and disposal in accordance with GOST 3.1603, GOST R 51769, GOST R 52108.
GOST R 22.1.13-2013
Basic provisions and requirements
1 The creation of structured systems for monitoring and management of engineering systems of buildings and structures (SMIS) is carried out in accordance with the requirements of documents on standardization in the field of civil defense, protection of the population and territories from emergencies and requirements for structured monitoring systems and management of engineering systems of buildings and structures.
2 Design documentation for SMIS is drawn up as a separate part "Design documentation of a structured monitoring and management system for engineering systems of buildings and structures" as part of the subsection "List of civil defense measures, measures to prevent natural and man-made emergencies", which is part of the section " Other documentation in cases stipulated by federal laws. "
3 In order to implement in the construction process the technical and technological solutions contained in the design documentation for SMIS, working documentation is being developed in accordance with GOST R 21.1101.
4 On the instructions of the developer (technical customer), special technical conditions for the creation and operation of SMIS (STU) can be developed. The recommended structure of the STU for the creation and operation of SMIS is presented in Appendix A (GOST R 22.1.13-2013).
The development of STU can also be carried out if the sources of natural and man-made threats to the building, structures are outside the design boundaries.
When determining the sources of emergency threats of a technogenic nature, it is advisable to take into account the facilities, engineering systems and structures specified in the list of types of work approved by the authorized federal executive body that affect the safety of capital construction facilities.
Justification of STU requirements is carried out in one or more of the following ways:
1) based on research results;
2) according to calculations and (or) tests performed according to certified or otherwise approved methods;
3) modeling of scenarios for the occurrence of hazardous natural processes and phenomena and (or) technogenic impacts, including with an unfavorable combination of hazardous natural processes and phenomena and (or) technogenic impacts;
4) an assessment of the risk of occurrence of hazardous natural processes and phenomena and (or) man-made impacts;
5) by the method of expert assessments.
Industrial safety declarations of hazardous production facilities developed in accordance with federal legislation, departmental, industry-specific safety regulations, subsections of the PM GOChS design documentation (if any) should be used as the initial data for the development of STUs.
Developers (technical customers) include the STU requirements in the technical specifications for the design of the SMIS and associated technological systems and engineering support systems, and also provide control over their implementation during design, construction, commissioning and operation.
5 Requirements in terms of organizing interaction and connecting the SMIS of the facility to the automated systems of the day-to-day management bodies of the RSChS shall be agreed with the authorized executive body of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation or the municipality, and in the cases provided for by law, with the territorial body of the EMERCOM of Russia in the corresponding constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
6 Design documentation for SMIS is developed in accordance with the initial data issued by the executive authority of the corresponding constituent entity of the Russian Federation, and in cases provided for by law, by the territorial body of the EMERCOM of Russia for the corresponding constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
7 Design solutions for SMIS ensure the implementation of the requirements for SMIS during the development of working documentation, during commissioning and operation of the facility.
8 Design and working documentation for SMIS is drawn up in accordance with state standards of the system of design documentation for construction (SPDS), the unified system for design documentation (ESKD) and other applicable regulatory documents and undergoes an examination in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
9 After receiving a positive expert opinion, one copy of the design documentation for SMIS as part of the PM GOChS subsection can be sent to the authorized body of the relevant constituent entity of the Russian Federation for the implementation, in the prescribed manner, of state supervision and control in the field of protecting the population and territories from natural and man-made emergencies during operation capital construction object.
Requirements for the procedure for creating and operating SMIS
1 Stages of creation and operation of SMIS
The creation and operation of the SMIS includes the following stages:
- preparation and receipt of initial data on the creation and operation of SMIS;
- development of STU for the creation and operation of SMIS (if necessary);
- development of technical specifications (TOR) for the design of SMIS;
- development of design documentation for SMIS;
- development of SMIS working documentation;
- work on the commissioning of the SMIS facility;
- operation of the SMIS facility.
Preparation and receipt of initial data for the creation and operation of SMIS
1 To ensure the creation and operation of the SMIS facility, the initial data include:
- initial data for the development of the GOChS PM;
- technical conditions for connecting the SMIS facility to the daily management bodies of the RSChS, technical conditions for communication and management in crisis situations in buildings and structures of the facility (if necessary);
- a list of threats, destabilizing factors, the control of which should be carried out by SMIS to prevent accidents, emergencies;
- general requirements for the scope of monitoring of SMIS of sources of emergency threats and destabilizing factors:
- technological systems (processes), systems of engineering and technical support of buildings and structures;
- engineering (supporting) structures and foundations of buildings and structures;
- hazardous natural processes and phenomena;
- requirements for the structure and procedure for the functioning of the SMIS;
- requirements for means of communication and information exchange of SMIS:
- between the components of the SMIS;
- with the daily management bodies of the RSChS;
- with controlled technological systems and systems of engineering and technical support of the facility;
- requirements for communication and management in crisis situations in buildings and structures of the facility;
- requirements for SMIS software and hardware complexes;
- requirements for the regulations of actions of the dispatching services of the facility, the daily management bodies of the RSChS when receiving messages from the SMIS;
- requirements for the regulations for ensuring the functioning of the communication and management system in crisis situations during the elimination of accidents, emergencies, fires at the facility;
- requirements for the procedure for the development, coordination and approval of SMIS documentation (design, working, operational);
- requirements for the list and content of measures to ensure the commissioning of the SMIS facility;
- requirements for the list and content of measures for the operation of the SMIS facility;
- additional requirements that are taken into account during the creation and operation of the SMIS.
2 The developer or technical customer of the design documentation, at the request of the SMIS developer, provides the preparation and issuance of initial data for the development of the SMIS.
3 The initial data for the design may include the initial data for the development of SMIS as part of the list of Civil Defense and Emergencies, issued by the authorized body. The list of initial data is given in Appendix B.
4 Qualification requirements for organizations that carry out design, commissioning and operation of SMIS are determined in accordance with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation in the field of urban planning, protection of the population and territories from emergencies, and industrial safety.
Qualification requirements for organizations carrying out work on the operation (use, maintenance and repair) of SMIS may include the availability of qualified specialists who have undergone training (training) in the prescribed manner and have a certificate (certificate) of advanced training in the relevant type of work.
5 The terms of reference for the design of SMIS is developed on the basis of GOST 34.602 and taking into account the requirements of STU for the creation and operation of SMIS (if they are developed), GOST R 22.1.12, this standard and other regulatory documents of the Russian Federation that establish requirements in the field of safety buildings and structures. The recommended structure of the TK for the design of SMIS is presented in Appendix D (GOST R 22.1.13).
6 In the technical conditions for connecting the SMIS facility to the day-to-day management bodies of the RSChS, information of an organizational and technical nature is provided, a list of works, the implementation of which at the stages of development of design, working documentation and commissioning ensures the connection and functioning of the SMIS in the RSChS (Appendix D (GOST R 22.1.13).
Requirements for the development of design documentation for SMIS
1 General requirements
1.1 Design documentation for SMIS is developed as part of:
- Book 1 "Subsystem of data collection and message transmission (SSP);
- Book 2 "Communication and management subsystem in crisis situations" (SUKS);
- Book 3 "Subsystem for monitoring engineering (bearing) structures, hazardous natural processes and phenomena" (SMIK), consisting of:
- Book 3.1 "Methods for monitoring the state of foundations, building structures, engineering protection structures, hazardous natural processes and phenomena";
- Book 3.2 "Engineering solutions for monitoring the state of foundations, building structures, engineering protection structures, hazardous natural processes and phenomena."
1.2 In the design solutions for interfacing with SMIS, set out in other sections of the design documentation of adjacent engineering systems, only the necessary information on the SMIS and descriptions of solutions for interfacing are provided with a mandatory reference to the design solutions of the subsection (part) "Design documentation of a structured monitoring and control system of engineering systems buildings and structures ".
1.3 The design documentation for the SMIS includes design solutions developed in accordance with STU for the creation and operation of the SMIS (if they are developed), the terms of reference for the design of the SMIS and in accordance with GOST R 22.1.12, GOST R 22.1. 02, GOST R 22.7.01, GOST 2.105, GOST 21.1101 *, GOST 24.701, GOST 27.003, GOST 21552, GOST 25861, GOST 12.1.030, GOST 12.2.003, GOST 12.2.007.0, GOST 20.39.108, GOST 27201, GOST 14254, GOST 3.1603, GOST R 51769, GOST R 52108, GOST R 22.0.10, GOST 34.602, GOST 34.201, taking into account "Methods for monitoring the state of load-bearing structures of buildings and structures", "Methods for assessing safety and life support systems at potentially hazardous facilities , buildings and structures "," Methods for assessing and certifying the engineering safety of buildings and structures ", regulatory legal and technical documents of organizations and departments on security issues of the subordinate construction facility.
2 Requirements for the structure and content of the book 1 "Subsystem of data collection and message transmission (SSP SMIS)"
2.1 Design solutions outlined in Book 1 include solutions:
a) on the detection of threats of accidents, emergencies for objects of control and destabilizing factors specified in GOST R 22.1.12, STU (if they are developed), technical specifications for the design of SMIS;
b) to ensure control of the main destabilizing factors specified in GOST R 22.1.12, STU (if they are developed), TOR for the design of SMIS;
c) to ensure that the daily management bodies of the RSChS perform forecasting and warning functions (including notification) of emergencies, emergencies, fires, as well as information support for decision-making on their elimination in accordance with the requirements of GOST R 22.1.12, STU (if they are developed ), Terms of Reference for the design of SMIS, including:
1) on the formation and transfer of information about a critical change in the state of engineering and technical support systems, the state of the foundation, building structures of buildings and structures, technological processes, engineering protection structures, incl. caused by terrorist acts;
2) documentation;
3) by recording on a protected medium of measured parameters of the state of engineering and technical support systems, the state of the foundation, building structures of buildings and structures, technological processes, engineering protection structures;
d) to ensure the implementation of the requirements for the software and hardware complexes of the BSC.
2.2 The structure of book 1 "Subsystem of data collection and message transmission (SSP)" is presented in Appendix E.
3 Requirements for the structure and content of the book 2 "Subsystem of communication and management in crisis situations of the object" (SUKS)
3.1 The design solutions set out in Book 2 ensure the fulfillment of the requirements and technical conditions for communication and control during the elimination of emergencies and emergencies at the facility.
4 Requirements for the structure and content of the book 3 "Subsystem for monitoring engineering (bearing) structures, hazardous natural processes and phenomena (SMIC)"
4.1 The design solutions outlined in Book 3 include:
a) solutions for monitoring and determining deviations of current values from standard parameters characterizing the state of foundations, building structures, engineering protection structures, hazardous natural processes and phenomena in the construction and operation area of the building (defined in STU, TZ);
b) decisions on information support for decision-making on the prevention and elimination of accidents, emergencies associated with changes in the state of foundations, building structures, engineering protection structures, hazardous natural processes and phenomena in the area of construction and operation of the building;
c) solutions that ensure the implementation of the requirements for the ISMS;
Requirements for the development of SMIS working documentation
1 SMIS working documentation is developed in accordance with the adopted design decisions for SMIS, taking into account the requirements set out in clause 6.3.1.3 of GOST R 22.1.13-2013.
The typical structure of the SMIS working documentation is presented in Appendix Zh (GOST R 22.1.13-2013).
2 At the stage of development of working documentation, as part of the operational documentation, regulations are developed for the DDS of the facility and the daily management bodies of the RSChS upon receipt of SMIS messages, regulations for ensuring the functioning of the communication and management system in crisis situations during the elimination of accidents, emergencies, fires, as well as the program and methodology for testing the SMIS in accordance with the requirements of GOST R 22.1.12, GOST 34.603, GOST 19.30, RD 50-34.698, "Methods for assessing security and life support systems at potentially hazardous facilities, buildings and structures."
5 Requirements for the list and content of work on the commissioning of the SMIS facility
1 Upon commissioning, work is carried out in accordance with the following list:
- preparation of the facility for the SMIS commissioning;
- personnel training;
- completing SMIS with products (software and hardware);
- construction and installation work;
- development of a passport for monitoring the state of foundations, building structures of buildings and structures, engineering protection structures, areas of mudflows, landslides, avalanches in the area of construction and operation of the facility;
- commissioning works;
- conducting preliminary tests;
- conducting trial operation (if necessary);
- Carrying out SMIS acceptance tests.
2 During acceptance tests of the SMIS, a list of documents must be submitted in accordance with Appendix I (GOST R 22.1.13-2013).
6 Requirements for SMIS facility operation
1 To ensure the functioning of the SMIS in accordance with its intended purpose, during its operation, work is carried out in accordance with the following list:
- control of technical condition;
- periodic maintenance;
- repair work;
- periodic, extraordinary monitoring of the state of engineering (bearing) structures, hazardous natural processes and phenomena;
- updating the monitoring passport based on the results of periodic (extraordinary) monitoring.
2 The list of SMIS operational documentation is given in Appendix K (GOST R 22.1.13-2013).
GOST R 22.1.12-2005, Safety in emergency situations. A structured system for monitoring and managing engineering systems of buildings and structures (SMIS). General requirements (with Amendment No. 1)
GOST R 22.1.13-2013, Safety in emergency situations. Civil defense measures, measures to prevent natural and man-made emergencies. A structured system for monitoring and managing engineering systems of buildings and structures (SMIS). Requirements for the order of creation and operation.
GOST R 22.1.14-2013, Safety in emergency situations. Complexes of information and computing structured monitoring systems and management of engineering systems of buildings and structures. Technical requirements. Test methods.
GOST R 22.1.15-2014, Safety in emergency situations. Technical means of monitoring natural and man-made emergencies. Classification. General technical requirements (Reissue).
GOST R 22.1.16-2015, Safety in emergency situations. Technical means of monitoring natural and man-made emergencies. Test methods.
GOST R 22.1.17-2016, Safety in emergency situations. A structured system for monitoring and managing engineering systems of buildings and structures (SMIS). Communication and crisis management system. General requirements.